How to handle missing data: A comparison of different approaches
Many researchers face the problem of missing data in longitudinal research. Especially, high risk samples are characterized by missing data which can complicate analyses and the interpretation of results.
Analyzing small data sets using Bayesian estimation: the case of posttraumatic stress symptoms following mechanical ventilation in burn survivors
The analysis of small data sets in longitudinal studies can lead to power issues and often suffers from biased parameter values. These issues can be solved by using Bayesian estimation in conjunction with informative prior distributions.
Latent Growth Mixture Models to estimate PTSD trajectories
Statistical models to estimate individual change over time and to investigate the existence of latent trajectories, where individuals belong to trajectories that are unobserved (latent), are becoming ever more popular.
Constrained statistical inference: sample-size tables for ANOVA and regression
Researchers in the social and behavioral sciences often have clear expectations about the order/direction of the parameters in their statistical model. For example, a researcher might expect that regression coefficient β1 is larger than β2 and β3.
Reducing bias due to systematic attrition in longitudinal studies: The benefits of multiple imputation
Most longitudinal studies are plagued by drop-out related to variables at earlier assessments (systematic attrition). Although systematic attrition is often analysed in longitudinal studies, surprisingly few researchers attempt to reduce biases due to systematic attrition, even though this is possible and nowadays technically easy.
A Gentle Introduction to Bayesian Analysis: Applications to Developmental Research
Bayesian statistical methods are becoming ever more popular in applied and fundamental research. In this study a gentle introduction to Bayesian analysis is provided. It is shown under what circumstances it is attractive to use Bayesian estimation, and how to interpret properly the results.
Bayesian analyses: where to start and what to report
Most researchers in the social and behavioral sciences will probably have heard of Bayesian statistics in which probability is defined differently compared to classical statistics (probability as the long-run frequency versus probability as the subjective experience of uncertainty).
Facing off with Scylla and Charybdis: a comparison of scalar, partial, and the novel possibility of approximate measurement invariance
Measurement invariance (MI) is a pre-requisite for comparing latent variable scores across groups. The current paper introduces the concept of approximate MI building on the work of Muthén and Asparouhov and their application of Bayesian Structural Equation Modeling (BSEM) in the software Mplus.
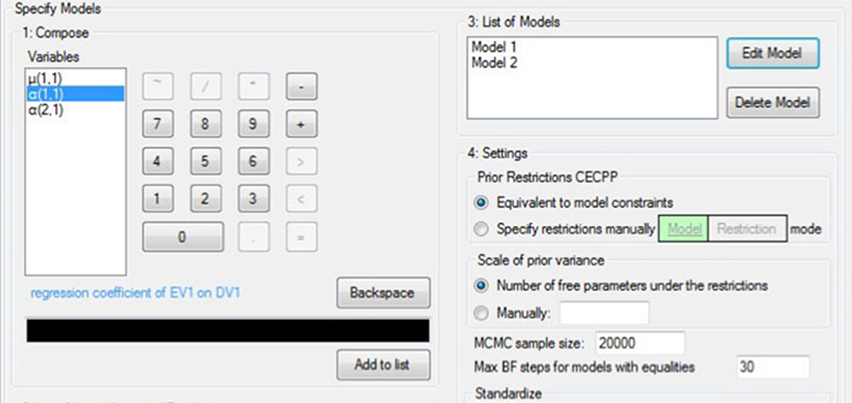
Bayesian evaluation of informative hypotheses in SEM using Mplus: A black bear story
Half in jest we use a story about a black bear to illustrate that there are some discrepancies between the formal use of the p-value and the way it is often used in practice. We argue that more can be learned from data by evaluating informative hypotheses, than by testing the traditional null hypothesis.
A checklist for testing measurement invariance
The analysis of measurement invariance of latent constructs is important in research across groups, or across time. By establishing whether factor loadings, intercepts and residual variances are equivalent in a factor model that measures a latent concept, we can assure that comparisons that are made on the latent variable are valid across groups or time.
Illustrating Bayesian evaluation of informative hypotheses for regression models
In the present article we illustrate a Bayesian method of evaluating informative hypotheses for regression models. Our main aim is to make this method accessible to psychological researchers without a mathematical or Bayesian background.