Improving Transparency and Replication in Bayesian Statistics: The WAMBS-Checklist
Bayesian statistical methods are slowly creeping into all fields of science and are becoming ever more popular in applied research. Although it is very attractive to use Bayesian statistics, our personal experience has led us to believe that naively applying Bayesian methods can be dangerous for at least 3 main reasons:
An Introduction to Bayesian Statistics in Health Psychology
Bayesian methods are increasing in prevalence in applied fields, and they have been shown in simulation research to improve the estimation accuracy of structural equation models, latent growth curve models, and hierarchical linear models.
A Systematic Review of Bayesian Papers in Psychology: The Last 25 Years
Although the statistical tools most often used by researchers in the field of psychology over the last 25 years are based on frequentist statistics, it is often claimed that the alternative Bayesian approach to statistics is gaining in popularity.
The GRoLTS-Checklist: Guidelines for Reporting on Latent Trajectory Studies
Estimating models within the mixture model framework, like latent growth mixture modeling (LGMM) or latent class growth analysis (LCGA), involves making various decisions throughout the estimation process. This has led to a wide variety in how results of latent trajectory analysis are reported.
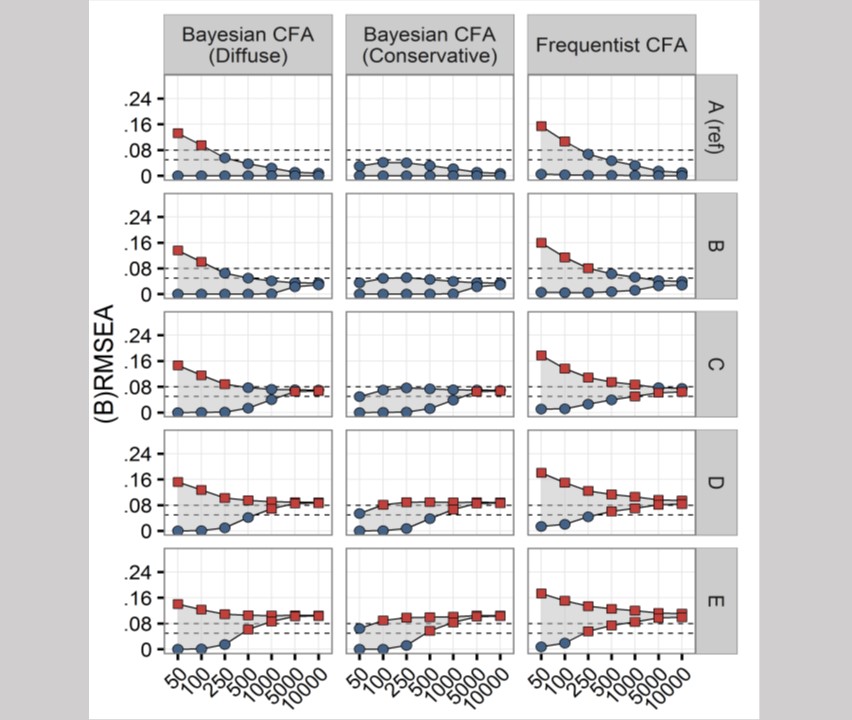
Simulation Study Introducing the BRMSEA
Evaluating model fit in Bayesian confirmatory factor analysis with large samples: Simulation study introducing the BRMSEA
Parents’ posttraumatic stress after burns in their school-aged child: A prospective study
Objective: This prospective study examined the course and potential predictors of parents’ posttraumatic stress symptoms (PTSS) after burn injury in their child (Age 8 to 18 years). Method: One hundred eleven mothers and 91 fathers, representing 118 children, participated in the study.
Computing complexity for the Bayes Factor in inequality constrained hypotheses
The computation of complexity for the Bayes Factor is described in this tutorial.
A coach in your pocket: on chronic cancer-related fatigue and physical behavior
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Wat zijn de regels van de wetenschap en liggen die voor altijd vast?
“Lang… lang geleden, in een dorp hier ver vandaan, stelden de eerste wetenschappers Vragen. Op een dag besloten zij dat Vragen stellen veel beter ging als ze zich terugtrokken uit het dorp en in een ivoren toren gingen werken. Daar konden zij in alle rust zoeken naar mogelijke antwoorden op de Vragen.
Application and Evaluation of an Expert Judgment Elicitation Procedure for Correlations
The purpose of the current study was to apply and evaluate a procedure to elicit expert judgments about correlations, and to update this information with empirical data. The result is a face-to-face group elicitation procedure with as its central element a trial roulette question that elicits experts’ judgments expressed as distributions.
Introducing the Fling – An Innovative Serious Game to Train Behavioral Control in Adolescents: Protocol of a Randomized Controlled Trial
Behavioral control weaknesses are a strong predictor of problematic behaviors in adolescents, such as heavy alcohol use. Heavy alcohol use at this young age can lead to health and school-related problems and is a severe societal problem.
A Bildung-psychological investigation into student motives: McKinsey- or von Humboldt-oriented?
This study examined differential student motives among students from a social sciences bachelor’s degree, and whether this difference related to participating in educational programmes for broader intellectual formation (Bildung). Survey research was conducted among 432 Dutch students (79.5% female), ranging in age from 17 to 32 years (Mage = 21.12, SD = 2.08).