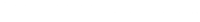Which School for Whom? Placement Choices for Inclusion or Exclusion of Dutch Students With Social, Emotional, and Behavioral Difficulties in Primary Education
This study examined which factors were related to placement choices for inclusive regular education or exclusive special education for Dutch students with social, emotional, and behavioral difficulties (SEBD).
Family scars after pediatric burns
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Making eye movements during imaginal exposure leads to short-lived memory effects compared to imaginal exposure alone
At intervention start, making EM during imaginal exposure prevents memory inflation. Imaginal exposure with or without EM causes immediate and 24 h memory deflation. Imaginal exposure + EM leads to short-lived effects compared to imaginal exposure. Change patterns were hardly explained by predictive variables.
Evaluation of two different Web-based interventions for chronic cancer-related fatigue
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Pushing the Limits
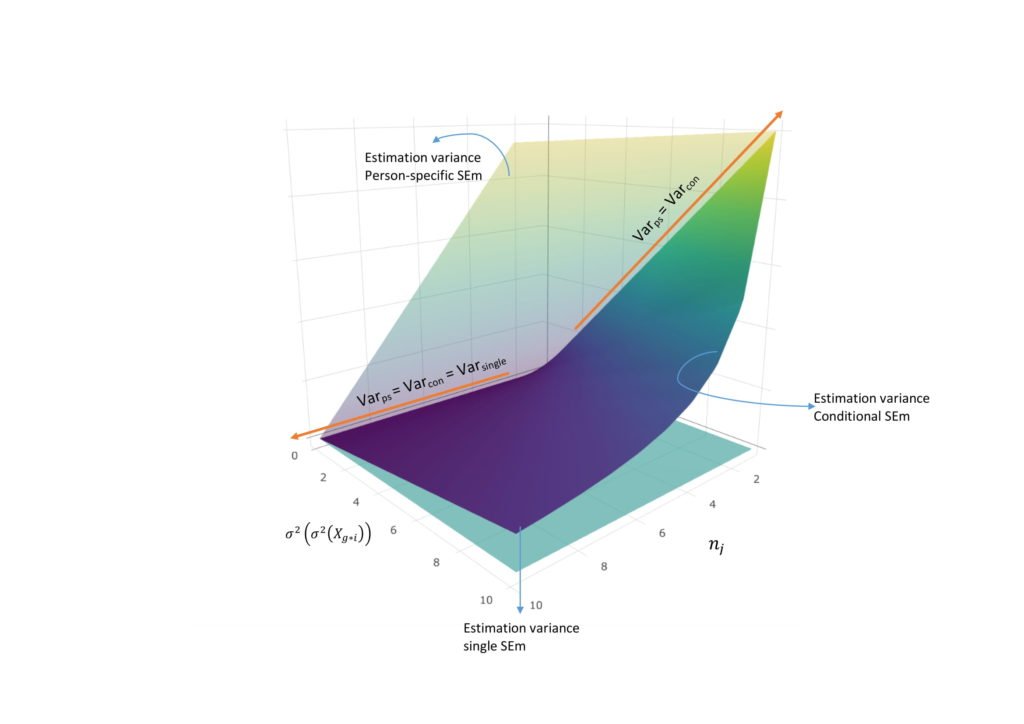
The Performance of Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Estimation With Small and Unbalanced Samples in a Latent Growth Model is compared in a simulation study
Development and Evaluation of a Digital Expert Elicitation Method
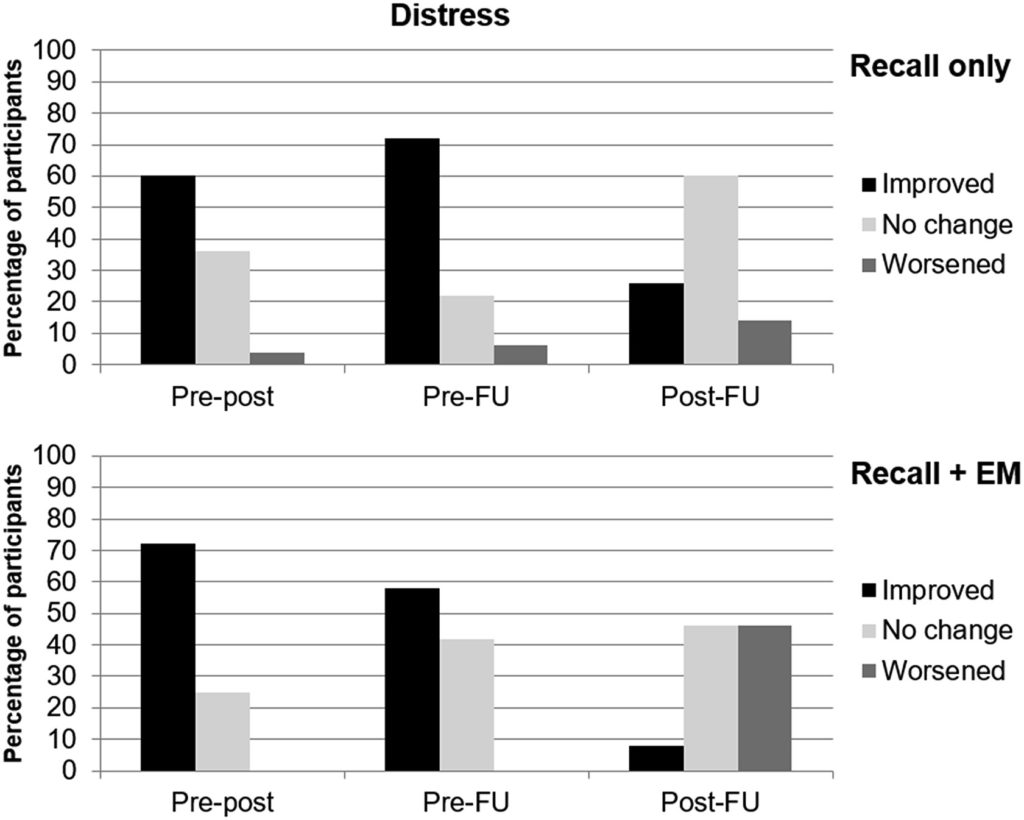
The paper describes an elicitation procedure which opens up many opportunities to investigate tacit differences between “subjective” teacher judgments and “objective” data such as test results and to raise the diagnostic competence of teachers.
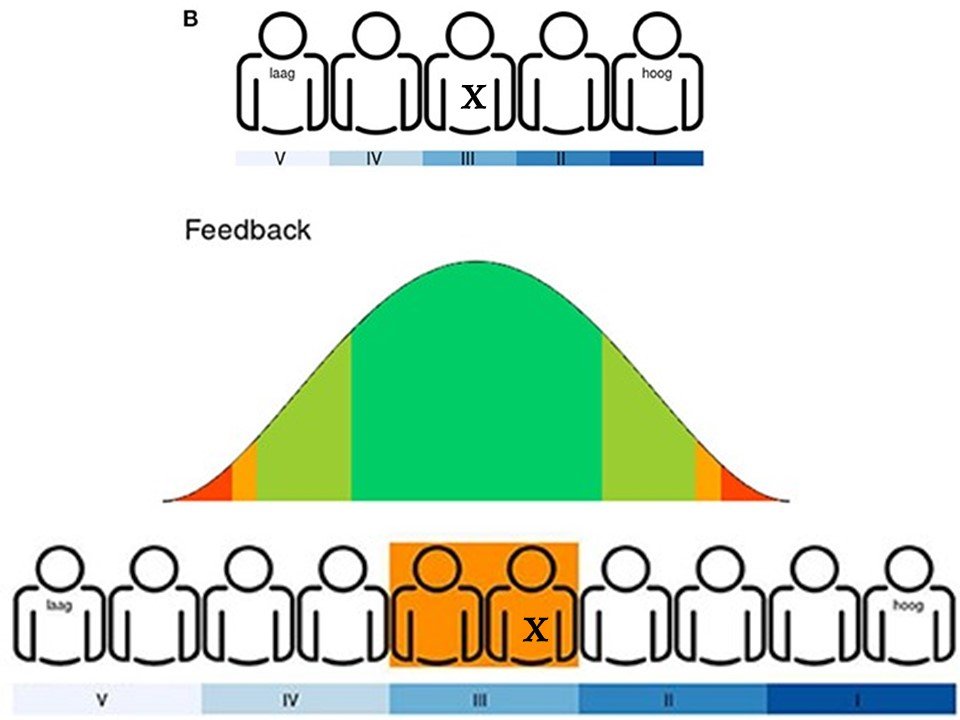
Testing Small Variance Priors Using Prior-Posterior Predictive P-values
Muthen and Asparouhov (2012) propose to evaluate model fit in structural equation models based on approximate (using small variance priors) instead of exact equality of (combinations of) parameters to zero. This is an important development that adequately addresses Cohen’s (1994) “The earth is round (p < .05)”, which stresses that point null-hypotheses are so precise that small and irrelevant differences from the null-hypothesis may lead to their rejection.
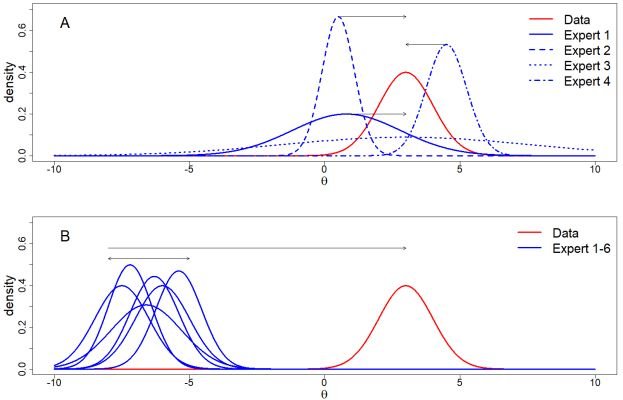
Using the Data Agreement Criterion to Rank Experts’ Beliefs
We evaluated priors based on expert knowledge by extending an existing prior-data (dis)agreement measure, the Data Agreement Criterion, and compare this approach to using Bayes factors to assess prior specification.
“Shape sorting” students for special education services?
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Manipulating the alpha level cannot cure significance testing
We argue that depending on p-values to reject null hypotheses, including a recent call for changing the canonical alpha level for statistical significance from .05 to .005, is deleterious for the finding of new discoveries and the progress of cumulative science.
Mother, father and child traumatic stress reactions after paediatric burn
The current study examined occurrence and within-family associations of traumatic stress reactions after child burn injury, while in the same model addressing the role of parents’ own symptoms in their reports of child symptoms.