Bayesian analyses: where to start and what to report
Most researchers in the social and behavioral sciences will probably have heard of Bayesian statistics in which probability is defined differently compared to classical statistics (probability as the long-run frequency versus probability as the subjective experience of uncertainty).
Facing off with Scylla and Charybdis: a comparison of scalar, partial, and the novel possibility of approximate measurement invariance
Measurement invariance (MI) is a pre-requisite for comparing latent variable scores across groups. The current paper introduces the concept of approximate MI building on the work of Muthén and Asparouhov and their application of Bayesian Structural Equation Modeling (BSEM) in the software Mplus.
What Took Them So Long? Explaining PhD Delays among Doctoral Candidates
A delay in PhD completion, while likely undesirable for PhD candidates, can also be detrimental to universities if and when PhD delay leads to attrition/termination. Termination of the PhD trajectory can lead to individual stress, a loss of valuable time and resources invested in the candidate and can also mean a loss of competitive advantage.
Bayesian evaluation of informative hypotheses in SEM using Mplus: A black bear story
Half in jest we use a story about a black bear to illustrate that there are some discrepancies between the formal use of the p-value and the way it is often used in practice. We argue that more can be learned from data by evaluating informative hypotheses, than by testing the traditional null hypothesis.
Bayesian Evaluation of Inequality-Constrained Hypotheses in SEM Models using Mplus
Researchers in the behavioral and social sciences often have expectations that can be expressed in the form of inequality constraints among the parameters of a structural equation model resulting in an informative hypothesis. The questions they would like an answer to are “Is the hypothesis Correct” or “Is the hypothesis incorrect”?
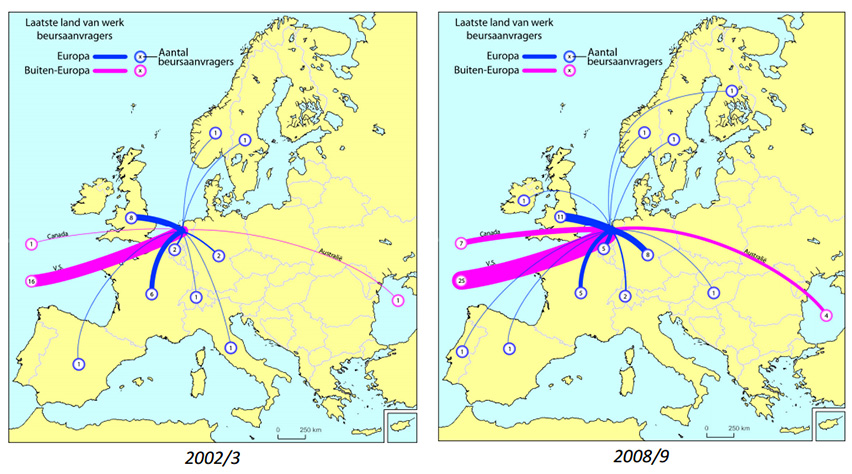
Mobiliteitsonderzoek Vernieuwingsimpuls-laureaten
In 2011 besloot NWO onderzoek te laten doen naar de wetenschappers die een subsidie ontvingen in het kader van de zogenoemde VernieuwingsImpuls (VI). Het gaat daarbij om drie typen subsidies die NWO als volgt omschrijft:
A checklist for testing measurement invariance
The analysis of measurement invariance of latent constructs is important in research across groups, or across time. By establishing whether factor loadings, intercepts and residual variances are equivalent in a factor model that measures a latent concept, we can assure that comparisons that are made on the latent variable are valid across groups or time.
The employment status of doctoral recipients: An exploratory study in the Netherlands
Studies of employment often focus on general labour market developments or the employment status of vulnerable groups concentrated at the lower end of the labour market. In contrast, the employment of highly educated individuals, in particular PhD recipients, has received less empirical attention.
Do Delinquent Young Adults have a High or a Low Level of Self-concept?
This study explored the levels of self-concept of delinquent young adults (n = 873). This question is of theoretical and practical importance, as therapeutic programs addressing the self-concept must be based on clear evidence.
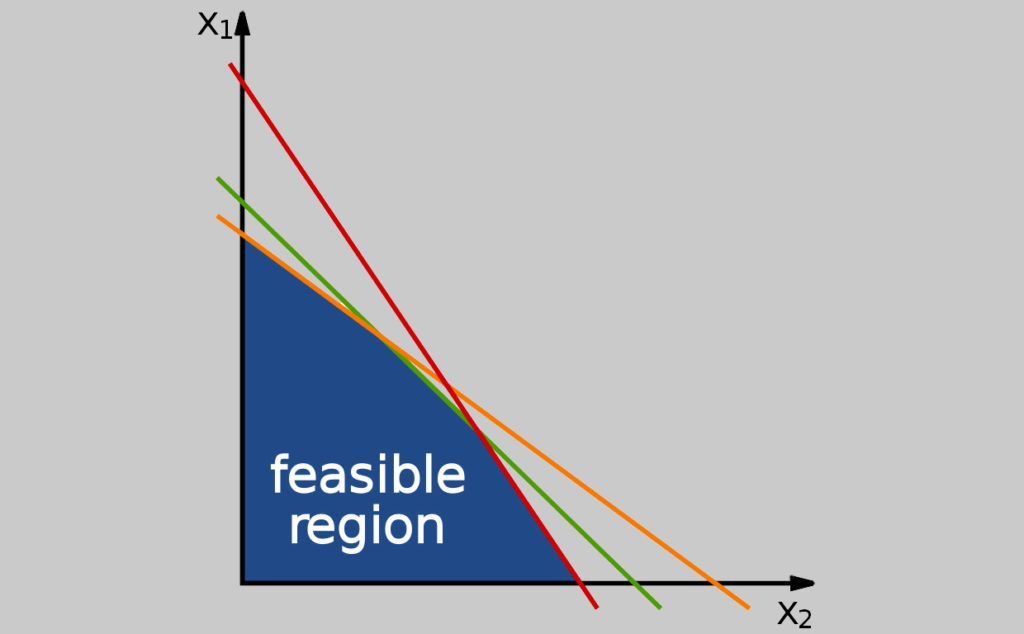
A prior predictive loss function for the evaluation of inequality constrained hypotheses
In many types of statistical modeling, inequality constraints are imposed between the parameters of interest. As we will show in this paper, the DIC (i.e., posterior Deviance Information Criterium as proposed as a Bayesian model selection tool by Spiegelhalter, Best, Carlin, & Van Der Linde, 2002) fails when comparing inequality constrained hypotheses.
An introduction to Bayesian model selection for evaluating informative hypotheses
Most researchers have specific expectations concerning their research questions. These may be derived from theory, empirical evidence, or both. Yet despite these expectations, most investigators still use null hypothesis testing to evaluate their data, that is, when analysing their data they ignore the expectations they have.