A Systematic Review of Bayesian Papers in Psychology: The Last 25 Years
Although the statistical tools most often used by researchers in the field of psychology over the last 25 years are based on frequentist statistics, it is often claimed that the alternative Bayesian approach to statistics is gaining in popularity.
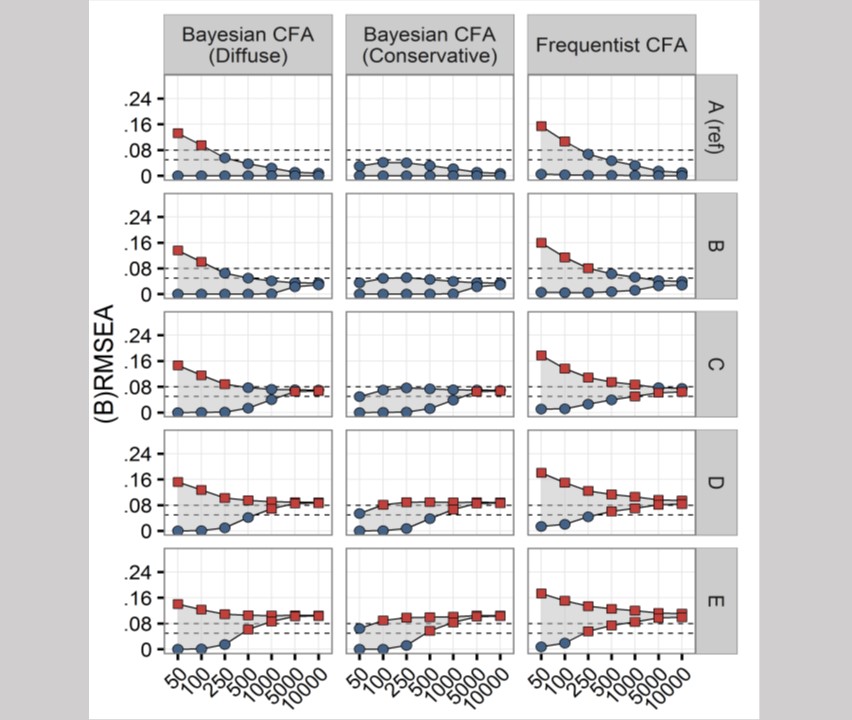
Simulation Study Introducing the BRMSEA
Evaluating model fit in Bayesian confirmatory factor analysis with large samples: Simulation study introducing the BRMSEA
Possible Solution to Publication Bias Through Bayesian Statistics
The present paper argues that an important cause of publication bias resides in traditional frequentist statistics forcing binary decisions. An alternative approach through Bayesian statistics provides various degrees of support for any hypothesis allowing balanced decisions and proper null hypothesis testing, which may prevent publication bias.
How to handle missing data: A comparison of different approaches
Many researchers face the problem of missing data in longitudinal research. Especially, high risk samples are characterized by missing data which can complicate analyses and the interpretation of results.
Effectiveness, Mediators, and Effect Predictors of Internet Interventions for Chronic Cancer-Related Fatigue
This paper describes the design and analysis plan that will be used to study 2 Internet interventions aimed at reducing severe fatigue in cancer survivors: a mobile ambulant activity feedback therapy supported through a weekly email by a physiotherapist and a weekly Web- and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy supported online by a psychologist.
Analyzing small data sets using Bayesian estimation: the case of posttraumatic stress symptoms following mechanical ventilation in burn survivors
The analysis of small data sets in longitudinal studies can lead to power issues and often suffers from biased parameter values. These issues can be solved by using Bayesian estimation in conjunction with informative prior distributions.
Social Influence Interpretation of Interpersonal Processes and Team Performance Over Time Using Bayesian Model Selection
The team behavior literature is ambiguous about the relations between members’ interpersonal processes—task debate and task conflict—and team performance. From a social influence perspective, we show why members’ interpersonal processes determine team performance over time in small groups.
Reducing bias due to systematic attrition in longitudinal studies: The benefits of multiple imputation
Most longitudinal studies are plagued by drop-out related to variables at earlier assessments (systematic attrition). Although systematic attrition is often analysed in longitudinal studies, surprisingly few researchers attempt to reduce biases due to systematic attrition, even though this is possible and nowadays technically easy.
The effectiveness of a proactive coping intervention targeting self-management in diabetes patients
The study’s aim was to investigate psychological, behavioral and medical long-term outcomes of an existing self-management intervention targeting the development of proactive coping skills (e.g. goal setting and identifying barriers) in type 2 diabetes patients.
Guilt in Bereavement: The Role of Self-Blame and Regret in Coping with Loss
Despite the apparent centrality of guilt in complicating reactions following bereavement, scientific investigation has been limited. Establishing the impact of specific components associated with guilt could enhance understanding.
A Gentle Introduction to Bayesian Analysis: Applications to Developmental Research
Bayesian statistical methods are becoming ever more popular in applied and fundamental research. In this study a gentle introduction to Bayesian analysis is provided. It is shown under what circumstances it is attractive to use Bayesian estimation, and how to interpret properly the results.
Bayesian analyses: where to start and what to report
Most researchers in the social and behavioral sciences will probably have heard of Bayesian statistics in which probability is defined differently compared to classical statistics (probability as the long-run frequency versus probability as the subjective experience of uncertainty).