Longitudinal Modeling
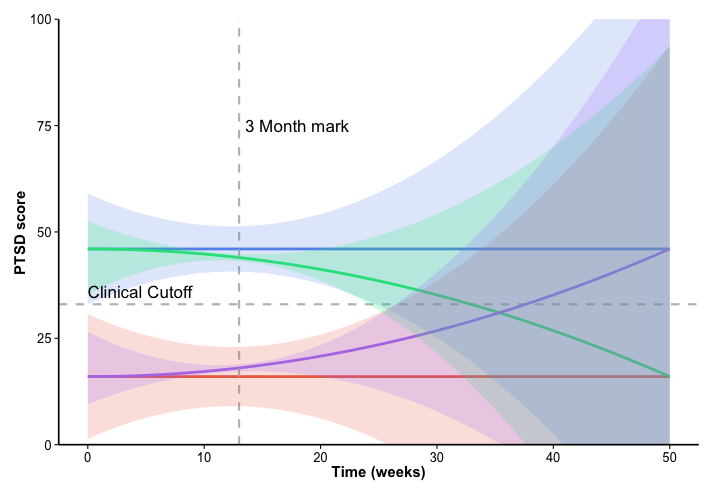
Typical for developmental psychology are models that capture change over time, such as latent growth (mixture) models and to a lesser extent cross-lagged panel models too. Such models have typically been applied aiming to capture change over time in individuals.
Small Samples
Researchers often have difficulties collecting enough data to obtain statistical power: when target groups are small (e.g., children with severe burn injuries), hard to access (e.g., infants of drug-dependent mothers), or measuring the participants requires prohibitive costs (e.g., measuring phonological difficulties of babies). Such obstacles to collecting data usually leads to a limited data set. Researchers can overcome this through simplifying their hypotheses and statistical models. However, this strategy is undesirable since the intended research question cannot be answered in this way.
My First Bayes
Since the beginning of the 21st century, Bayesian statistical methods are slowly creeping into all fields of science and are becoming ever more popular in applied research.
A coach in your pocket: on chronic cancer-related fatigue and physical behavior
In this dissertation, we focused on two alternative approaches to evaluate the hypothesis of interest more directly, i.e. informative hypothesis testing and model selection using order-restricted information criteria.
Symposium at M3 conference accepted
Bayes is growing in all disciplines! This is one of the results found by van de Schoot, Winter, Ryan, Zondervan-Zwijnenburg and Depaoli (in press) in an extensive systematic review.
Presentation about GRoLTS-Checklist
At the Meeting of the Working Group SEM (16 and 17 March 2017; Ghent, Belgium) I will present about the Guidelines for Reporting on Latent Trajectory Studies. March 16 at 14:15-14:45 Abstract: Estimating models within the mixture model framework, like Latent Growth Mixture Modeling (LGMM) or Latent Class…
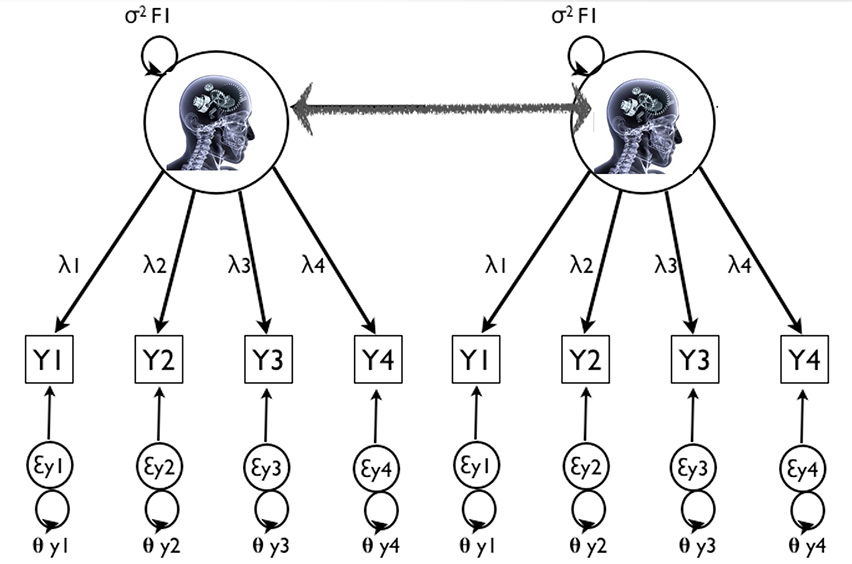
Measurement Invariance
To assess the presence of abstract concepts in people, like prolonged grief disorder, peritraumatic dissociation and students’ motivation, surveys can be used. When concepts are operationalized by means of questions or “items”, they are called “latent variables”.
APS symposium accepted: “Experts and Animals: How Can They Help Us?”
How and to what extend can we use the unique information derived from experts and animals? We discuss how expert opinions can be formalized and included in analyses, how animal studies can provide insight into human behavior, and ways to compare results from these sources…
Beyond Null Hypthesis Testing
Many researchers have no particular interest in a null hypothesis assuming that “nothing is going on”, so why test it at all? Evaluating specific, directional expectations produces more insightful results than sequentially testing traditional null hypotheses against catch-all rivals.
Expert Data (Dis)agreement
Elicitation is the process of extracting knowledge about the parameters in the statistical model. This information can then be used to provide input for the prior distribution needed for Bayesian analysis. Several methods of prior elicitation are used in practice including the use of experts.
Livingroom of Science
Science is a dynamic process with continuously developing, often implicit rules and attitudes. Proclamations such as “this is how we always do it”, “get used to it”, or “this is what it takes to grow in academia” occur more frequently than they ideally should.
Application and Evaluation of an Expert Judgment Elicitation Procedure for Correlations
The purpose of the current study was to apply and evaluate a procedure to elicit expert judgments about correlations, and to update this information with empirical data. The result is a face-to-face group elicitation procedure with as its central element a trial roulette question that elicits experts’ judgments expressed as distributions.