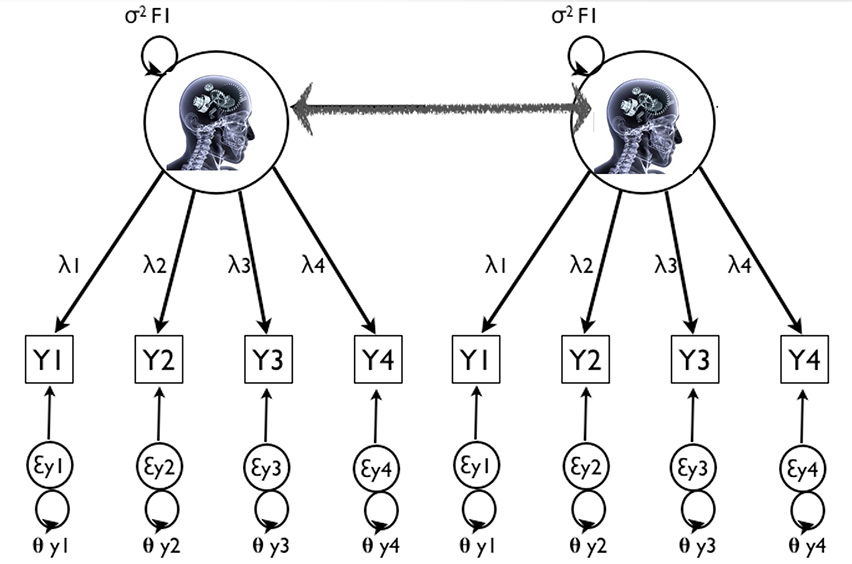
PTSD Symptom Trajectories in Disaster Volunteers: The Role of Self-Efficacy, Social Acknowledgement, and Tasks Carried Out
Millions of volunteers respond after disasters, with a 24% to 46% risk of developing posttraumatic stress disorder (PTSD). It is unclear which symptom trajectories develop and how they differ between core (volunteering before the disaster) and noncore volunteers (joining after the disaster) and which factors predict trajectories.
The Stability of Problem Behavior Across the Preschool Years: An Empirical Approach in the General Population
This study examined the stability of internalizing and externalizing problems from age 1.5 to 6 years, while taking into account developmental changes in the presentation of problems. The study comprised a population-based cohort of 7,206 children (50.4 % boys).
Direct Aggression and Generalized Anxiety in Adolescence: Heterogeneity in Development and Intra-Individual Change
Co-occurrence of aggression and anxiety might change during adolescence, or stay stable. We studied change and stability of four types of co-occurrence regarding direct aggression and anxiety in adolescence: an anxious and non-aggressive type, an aggressive and non-anxious type, a comorbid aggressive-anxious type and a no problems type.
VI European Congress of Methodology
From July 23 to 25, 2014, the VI European Congress of Methodology was held in Utrecht, the Netherlands. The European Congress of Methodology is organized biennially under the supervision of the European Association of Methodology (EAM), a society established in 2004, which brings together a large number of researchers from all over the world.
Possible Solution to Publication Bias Through Bayesian Statistics
The present paper argues that an important cause of publication bias resides in traditional frequentist statistics forcing binary decisions. An alternative approach through Bayesian statistics provides various degrees of support for any hypothesis allowing balanced decisions and proper null hypothesis testing, which may prevent publication bias.
Measurement Invariance (book)
Multi-item surveys are frequently used to study scores on latent factors, like human values, attitudes and behavior. Such studies often include a comparison, between specific groups of individuals, either at one or multiple points in time.
How to handle missing data: A comparison of different approaches
Many researchers face the problem of missing data in longitudinal research. Especially, high risk samples are characterized by missing data which can complicate analyses and the interpretation of results.
Collinear Latent Variables in Multilevel Confirmatory Factor Analysis: A Comparison of Maximum Likelihood and Bayesian Estimation
Because variables may be correlated in the social and behavioral sciences, multicollinearity might be problematic. This study investigates the effect of collinearity manipulated in within and between levels of a two-level confirmatory factor analysis by Monte Carlo simulation.
Effectiveness, Mediators, and Effect Predictors of Internet Interventions for Chronic Cancer-Related Fatigue
This paper describes the design and analysis plan that will be used to study 2 Internet interventions aimed at reducing severe fatigue in cancer survivors: a mobile ambulant activity feedback therapy supported through a weekly email by a physiotherapist and a weekly Web- and mindfulness-based cognitive therapy supported online by a psychologist.
Individual and class room predictors of same-cultural friendship preferences in multicultural schools
This study was an investigation of individual and contextual predictors for same-cultural friendship preferences among non-immigrant (n = 125), Turkish (n = 196) and former Yugoslavian (n = 256) immigrant youths (Mage= 14.39 years) in 36 multicultural classes.
Analyzing small data sets using Bayesian estimation: the case of posttraumatic stress symptoms following mechanical ventilation in burn survivors
The analysis of small data sets in longitudinal studies can lead to power issues and often suffers from biased parameter values. These issues can be solved by using Bayesian estimation in conjunction with informative prior distributions.